题目描述
请按下列描述构建一颗二叉树,并返回该树的根节点:
1、先创建值为-1的根结点,根节点在第0层;
2、然后根据operations依次添加节点: operations[i] = [height, index] 表示对第 height 层的第index 个节点node, 添加值为 i 的子节点:
- 若node 无「左子节点」,则添加左子节点;
- 若node 有「左子节点」,但无「右子节点」,则添加右子节点;
- 否则不作任何处理。
height、index 均从0开始计数;
index 指所在层的创建顺序。
注意:
- 输入用例保证每次操作对应的节点已存在;
- 控制台输出的内容是根据返回的树根节点,按照层序遍历二叉树打印的结果。
输入描述
operations
输出描述
根据返回的树根节点,按照层序遍历二叉树打印的结果
备注
- 1 <= operations.length <= 100
- operations[i].length == 2
- 0 <= operations[i][0] < 100
- 0 <= operations[i][1] < 100
用例
| 输入 | [[0, 0], [0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 0], [0, 0]] |
| 输出 | [-1, 0, 1, 3, null, 2] |
| 说明 |
首个值是根节点的值,也是返回值; null 表示是空节点,此特殊层序遍历会遍历有值节点的 null 子节点 |
| 输入 | [[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 0], [2, 1], [2, 1], [2, 1], [2, 0], [3, 1], [2, 0]] |
| 输出 | [-1, 0, null, 1, 2, 6, 8, 3, 4, null, null, null, null, null, null, 7] |
| 说明 |
首个值是根节点的值,也是返回值; null 表示是空节点,此特殊层序遍历会遍历有值节点的 null 子节点 |
题目解析
首先,解释下上面两个用例的输入,输出
用例1含义

operations[0] = [0, 0]
即:第0行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值0

operations[1] = [0, 0]
即:第0行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值1
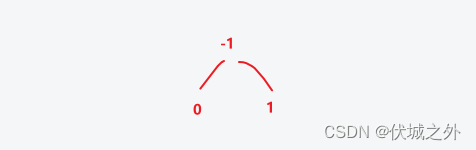
operations[2] = [1, 1]
即:第1行第1个创建的节点插入子节点值2
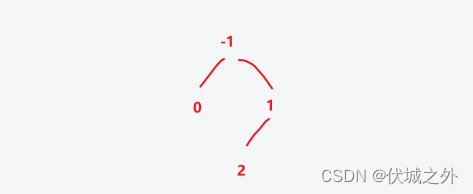
operations[3] = [1, 0]
即:第1行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值3
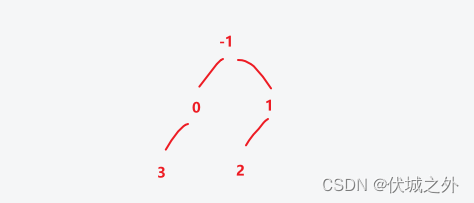
operations[4] = [0, 0]
即:第0行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值4,但是由于第0行第0个创建的节点左右子节点都已有了,因此不插入
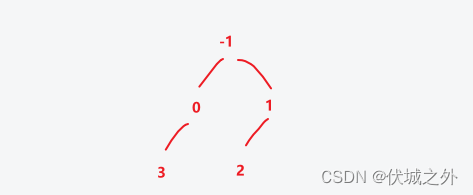
上图就是用例1的二叉树,输出时,由于题目说:层序遍历会遍历有值节点的 null 子节点,因此为上面二叉树的有值节点加入null子节点,如下图所示
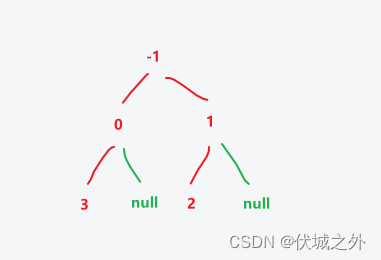
层序遍历结果为:-1, 0, 1, 3, null, 2, null
但是用例输出是:[-1, 0, 1, 3, null, 2],因此最后一个null子节点可以不用输出。
用例2含义

operations[0] = [0, 0]
即:第0行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值0

operations[1] = [1, 0]
即:第1行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值1
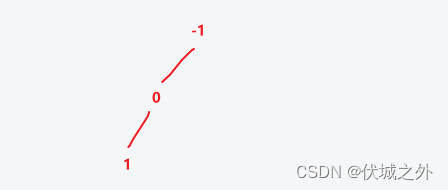
operations[2] = [1, 0]
即:第1行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值2
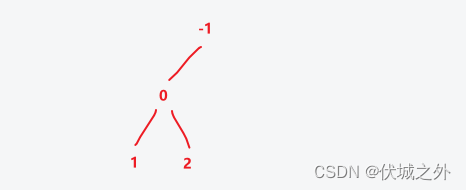
operations[3] = [2, 1]
即:第2行第1个创建的节点插入子节点值3
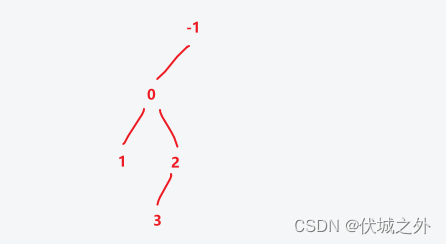
operations[4] = [2, 1]
即:第2行第1个创建的节点插入子节点值4
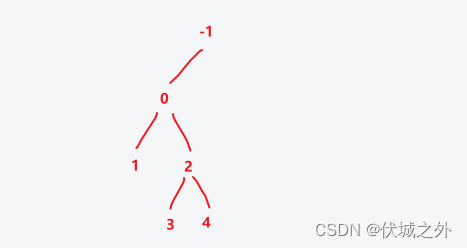
operations[5] = [2, 1]
即:第2行第1个创建的节点插入子节点值5,但是由于第2行第1个创建的节点已经有了左右子节点,因此不插入
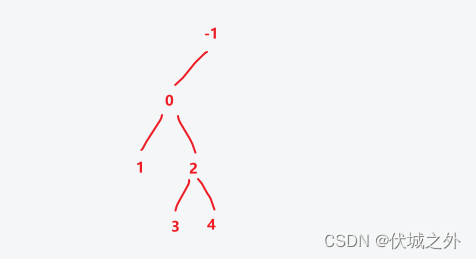
operations[6] = [2, 0]
即:第2行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值6
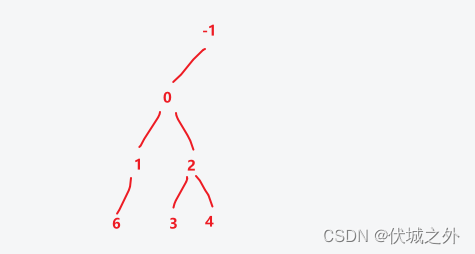
operations[7] = [3, 1]
即:第3行第1个创建的节点插入子节点值7
此时需要特别注意下,第3行第1个创建的节点是上图的值3节点吗????
为什么我要特别标注这句话呢?
因为题目中说:operations[i] = [height, index],而index 指所在层的创建顺序。
我们回到 operations[4],可以发现第3行第1个创建的节点是值4节点,而值3节点是第3行第0个创建的节点。
因此此步图示如下
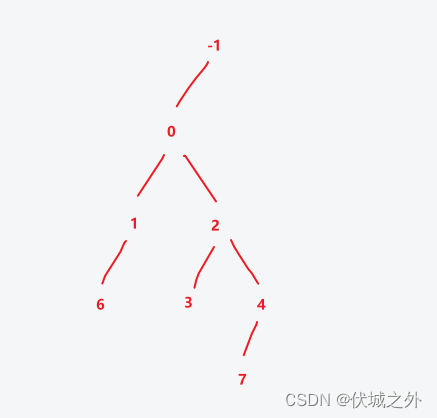
operations[8] = [2, 0]
即:第2行第0个创建的节点插入子节点值8
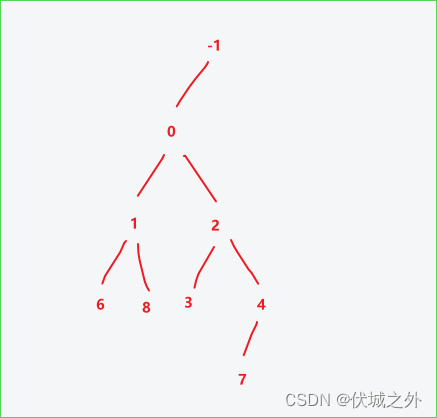
补充有值节点的null子节点
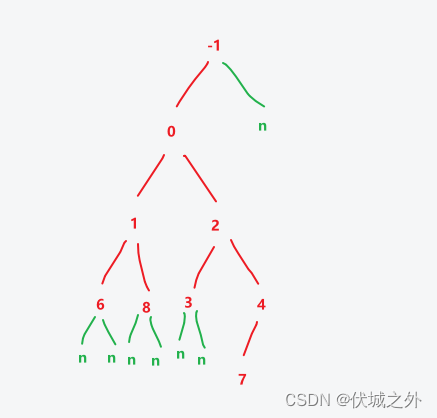
因此按照层序输出顺序是:
-1, 0, null, 1, 2, 6, 8, 3, 4, null, null, null, null, null, 7
当我们了解完上面两个用例的含义后,就可以做题了。
本题的难点在于如何记录每层节点的创建顺序index,如果通过传统的二叉树结构,则很难实现,原因是:
- 如何通过height(层数),index(该层第index个创建的)对应到二叉树的点
其中层数height可以通过层序遍历二叉树找到,但是index创建顺序却无法通过层序遍历找到,因此在构建二叉树时,还需要额外记录index到每个点自身,在层序遍历的时候,找到点,并取得它自身记录的index值,对比要查找的index值。
上面这个逻辑就非常麻烦了,因此不推荐这么做。
我的解题思路是,创建一个二维数组(集合,列表)tree,初始时为: [[node(-1)]]
即tree[0][0] = node(-1),这里tree[0][0]表示height = 0, index = 0
即tree的行索引就是height层数,列索引就是index创建顺序
tree[0][0]就代表二叉树根节点。
当我们遍历operations时,operations[i] = [height, index] ,其实就是找 tree[height][index]父节点,在该父节点下插入node(i)子节点,而在该父节点下插入node(i)子节点,其实就是向tree[height+1]数组中加入node(i)节点,比如
插入逻辑是:
- 若tree[height][index] 无「左子节点」,则添加左子节点;
- 若tree[height][index] 有「左子节点」,但无「右子节点」,则添加右子节点;
- 否则不作任何处理。
如果tree[height+1]不存在,需要先初始化一个数组,然后加入node(i)节点,此时node(i)节点在tree[height+1]中的索引其实就是node(i)节点,在height+1层的index创建顺序。
这样的话,我们就能依赖于tree二维数组结构来完成任意节点的height,index的记录了。这样用例2插入值7时,就可以快速找到第3行第1个创建的节点了。
但是,此时各节点之间并没有建立连续,因此我们还要设计Node类,来完成各节点之间的父子关系构建。这个就很简单了,具体实现看代码。
2023.03.15 经网友指正,有如下用例:
[[0,0],[0,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[2,2]]
其中[2,2]应该对应哪个值得节点,大家可以先思考一下

其实如果按照上面思路,值4节点应该是二叉树的第二行第二个创建的节点,但是它没有成功插入到二叉树中。
因此它不能算二叉树的第二行第二个创建的节点,值5接待你才能算上二叉树的第二行第二个创建的节点。
因此,前面tree记录节点创建顺序时,应该注意这种情况,要排除掉加入二叉树失败的节点。
JavaScript算法源码
/* JavaScript Node ACM模式 控制台输入获取 */
const readline = require("readline");
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
rl.on("line", (line) => {
const operations = JSON.parse(line);
console.log(getResult(operations));
});
function getResult(operations) {
const tree = [[new Node(-1)]];
for (let i = 0; i < operations.length; i++) {
const [height, index] = operations[i];
if (!tree[height + 1]) tree.push([]);
const ch = new Node(i);
const fa = tree[height][index];
// 注意,tree用于记录树中加入成功的节点是第几行第几个创建的,对于加入的失败的不应该记录
if (fa.lc == null || fa.rc == null) {
tree[height + 1].push(ch);
}
if (!fa.lc) fa.lc = ch;
else if (!fa.rc) fa.rc = ch;
}
const ans = [];
const queue = [tree[0][0]];
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node) {
ans.push(node.val);
queue.push(node.lc);
queue.push(node.rc);
} else {
ans.push(null);
}
}
while (true) {
if (ans.at(-1) == null) ans.pop();
else break;
}
return JSON.stringify(ans).replace(/,/g, ", ");
}
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.lc = null;
this.rc = null;
}
}
Java算法源码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
Integer[][] operations =
Arrays.stream(str.substring(1, str.length() - 1).split("(?<=]), (?=\[)"))
.map(
s ->
Arrays.stream(s.substring(1, s.length() - 1).split(", "))
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.toArray(Integer[]::new))
.toArray(Integer[][]::new);
System.out.println(getResult(operations));
}
public static String getResult(Integer[][] operations) {
Node head = new Node(-1);
ArrayList<Node> level0 = new ArrayList<>();
level0.add(head);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> tree = new ArrayList<>();
tree.add(level0);
for (int i = 0; i < operations.length; i++) {
int height = operations[i][0];
int index = operations[i][1];
if (tree.size() <= height + 1) {
tree.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
Node ch = new Node(i);
Node fa = tree.get(height).get(index);
// 注意,tree用于记录树中加入成功的节点是第几行第几个创建的,对于加入的失败的不应该记录
if (fa.lc == null || fa.rc == null) {
tree.get(height + 1).add(ch);
}
if (fa.lc == null) fa.lc = ch;
else if (fa.rc == null) fa.rc = ch;
}
LinkedList<Integer> ans = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(tree.get(0).get(0));
while (queue.size() > 0) {
Node node = queue.removeFirst();
if (node != null) {
ans.add(node.val);
queue.add(node.lc);
queue.add(node.rc);
} else {
ans.add(null);
}
}
while (true) {
if (ans.getLast() == null) ans.removeLast();
else break;
}
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(", ", "[", "]");
for (Integer an : ans) {
sj.add(an + "");
}
return sj.toString();
}
}
class Node {
int val;
Node lc;
Node rc;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.lc = null;
this.rc = null;
}
}
Python算法源码
# 输入获取
operations = eval(input())
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.lc = None
self.rc = None
# 算法入口
def getResult(operations):
tree = [[Node(-1)]]
for i in range(len(operations)):
height, index = operations[i]
if len(tree) <= height + 1:
tree.append([])
ch = Node(i)
fa = tree[height][index]
# 注意,tree用于记录树中加入成功的节点是第几行第几个创建的,对于加入的失败的不应该记录
if not fa.lc or not fa.rc:
tree[height + 1].append(ch)
if not fa.lc:
fa.lc = ch
elif not fa.rc:
fa.rc = ch
ans = []
queue = [tree[0][0]]
while len(queue) > 0:
node = queue.pop(0)
if node is not None:
ans.append(node.val)
queue.append(node.lc)
queue.append(node.rc)
else:
ans.append("null")
while True:
if ans[-1] == "null":
ans.pop()
else:
break
return ans
# 算法调用
res = str(getResult(operations))
print(res.replace("'", ""))
免责声明:
评论0