题目描述
网络信号经过传递会逐层衰减,且遇到阻隔物无法直接穿透,在此情况下需要计算某个位置的网络信号值。
注意:网络信号可以绕过阻隔物。
array[m][n] 的二维数组代表网格地图,
array[i][j] = 0代表i行j列是空旷位置;
array[i][j] = x(x为正整数)代表i行j列是信号源,信号强度是x;
array[i][j] = -1代表i行j列是阻隔物。
信号源只有1个,阻隔物可能有0个或多个
网络信号衰减是上下左右相邻的网格衰减1
现要求输出对应位置的网络信号值。
输入描述
输入为三行,第一行为 m 、n ,代表输入是一个 m × n 的数组。
第二行是一串 m × n 个用空格分隔的整数.
每连续 n 个数代表一行,再往后 n 个代表下一行,以此类推。
对应的值代表对应的网格是空旷位置,还是信号源,还是阻隔物。
第三行是 i 、 j,代表需要计算array[i][j]的网络信号值。
注意:此处 i 和 j 均从 0 开始,即第一行 i 为 0。
例如
6 50 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 01 4
代表如下地图
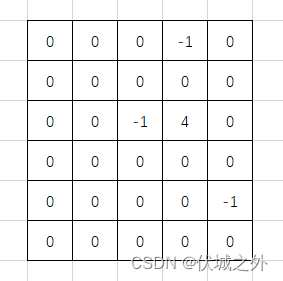
需要输出第1行第4列的网络信号值,如下图,值为2。
输出描述
输出对应位置的网络信号值,如果网络信号未覆盖到,也输出0。
一个网格如果可以途径不同的传播衰减路径传达,取较大的值作为其信号值。
用例
| 输入 | 6 5 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 1 4 |
| 输出 | 2 |
| 说明 | 无 |
| 输入 | 6 5 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 |
| 输出 | 0 |
| 说明 | 无 |
题目解析
用例图示如下
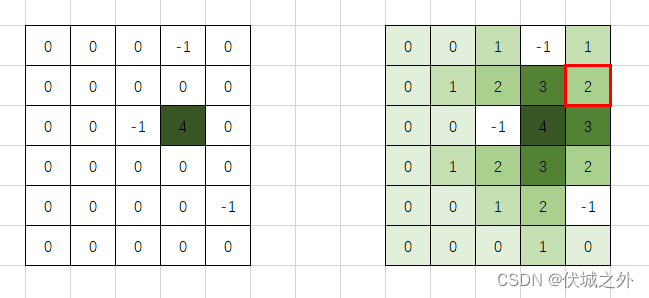
因此[1,4]位置(如上图红框位置)的值为2。
通过图示,我们可以很容易想到解题思路是图的多源BFS。
因此,题解请参考:
JavaScript算法源码
/* JavaScript Node ACM模式 控制台输入获取 */
const readline = require("readline");
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
const lines = [];
rl.on("line", (line) => {
lines.push(line);
if (lines.length === 3) {
const [m, n] = lines[0].split(" ").map(Number);
const arr = lines[1].split(" ").map(Number);
const pos = lines[2].split(" ").map(Number);
console.log(getResult(arr, m, n, pos));
lines.length = 0;
}
});
function getResult(arr, m, n, pos) {
let queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[i * n + j] > 0) {
queue.push([i, j]);
break;
}
}
}
// 上下左右偏移量
const offset = [
[-1, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, -1],
[0, 1],
];
while (queue.length) {
const newQueue = []; // 此时不使用queue.shift操作,因为此步操每次都需要O(n)时间,无法应对大数量级情况
for (const [i, j] of queue) {
const x = arr[i * n + j] - 1;
if (x === 0) break;
for (let [offsetX, offsetY] of offset) {
const newI = i + offsetX;
const newJ = j + offsetY;
if (
newI >= 0 &&
newI < m &&
newJ >= 0 &&
newJ < n &&
arr[newI * n + newJ] === 0
) {
arr[newI * n + newJ] = x;
newQueue.push([newI, newJ]);
}
}
}
queue = newQueue;
}
const [tarI, tarJ] = pos;
return arr[tarI * n + tarJ];
}
Java算法源码
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[m * n];
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int tarI = sc.nextInt();
int tarJ = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(getResult(arr, m, n, tarI, tarJ));
}
public static int getResult(int[] arr, int m, int n, int tarI, int tarJ) {
LinkedList<Integer[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[i * n + j] > 0) {
queue.addLast(new Integer[] {i, j});
break;
}
}
}
// 上下左右偏移量
int[][] offsets = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
while (queue.size() > 0) {
Integer[] pos = queue.removeFirst();
int i = pos[0];
int j = pos[1];
int x = arr[i * n + j] - 1;
if (x == 0) break;
for (int[] offset : offsets) {
int newI = i + offset[0];
int newJ = j + offset[1];
if (newI >= 0 && newI < m && newJ >= 0 && newJ < n && arr[newI * n + newJ] == 0) {
arr[newI * n + newJ] = x;
queue.addLast(new Integer[] {newI, newJ});
}
}
}
return arr[tarI * n + tarJ];
}
}
Python算法源码
# 输入获取
m, n = map(int, input().split())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
pos = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 算法入口
def getResult(arr, m, n, pos):
queue = []
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if arr[i * n + j] > 0:
queue.append([i, j])
break
offsets = ((-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1))
while len(queue) > 0:
newQueue = []
for i, j in queue:
x = arr[i * n + j] - 1
if x == 0:
break
for offsetX, offsetY in offsets:
newI = i + offsetX
newJ = j + offsetY
if 0 <= newI < m and 0 <= newJ < n and arr[newI * n + newJ] == 0:
arr[newI * n + newJ] = x
newQueue.append([newI, newJ])
queue = newQueue
tarI, tarJ = pos
return arr[tarI * n + tarJ]
# 算法调用
print(getResult(arr, m, n, pos))
C算法源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct ListNode {
int ele;
struct ListNode *next;
} ListNode;
typedef struct {
int size;
ListNode *head;
ListNode *tail;
} LinkedList;
LinkedList *new_LinkedList();
void addLast_LinkedList(LinkedList *link, int ele);
int removeFirst_LinkedList(LinkedList* link);
int getResult(int nums[], int m, int n, int tarI, int tarJ);
int main() {
int m, n;
scanf("%d %d", &m, &n);
int nums[m*n];
for(int i=0; i<m*n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &nums[i]);
}
int tarI, tarJ;
scanf("%d %d", &tarI, &tarJ);
printf("%dn", getResult(nums, m, n, tarI, tarJ));
return 0;
}
int getResult(int nums[], int m, int n, int tarI, int tarJ) {
LinkedList* queue = new_LinkedList();
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
if(nums[i * n + j] > 0) {
addLast_LinkedList(queue, i * n + j);
break;
}
}
}
int offsets[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
while(queue->size > 0) {
int pos = removeFirst_LinkedList(queue);
int i = pos / n;
int j = pos % n;
int x = nums[i * n + j] - 1;
if(x == 0) break;
for(int k=0; k<4; k++) {
int newI = i + offsets[k][0];
int newJ = j + offsets[k][1];
if(newI >= 0 && newI < m && newJ >= 0 && newJ < n && nums[newI * n + newJ] == 0) {
nums[newI * n + newJ] = x;
addLast_LinkedList(queue, newI * n + newJ);
}
}
}
return nums[tarI * n + tarJ];
}
LinkedList *new_LinkedList() {
LinkedList *link = (LinkedList *) malloc(sizeof(LinkedList));
link->size = 0;
link->head = NULL;
link->tail = NULL;
return link;
}
void addLast_LinkedList(LinkedList *link, int ele) {
ListNode *node = (ListNode *) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->ele = ele;
node->next = NULL;
if (link->size == 0) {
link->head = node;
link->tail = node;
} else {
link->tail->next = node;
link->tail = node;
}
link->size++;
}
int removeFirst_LinkedList(LinkedList* link) {
if(link->size == 0) exit(-1);
ListNode* removed = link->head;
if(link->size == 1) {
link->head = NULL;
link->tail = NULL;
} else {
link->head = link->head->next;
}
link->size--;
int res = removed->ele;
free(removed);
return res;
}
免责声明:
1、IT资源小站为非营利性网站,全站所有资料仅供网友个人学习使用,禁止商用
2、本站所有文档、视频、书籍等资料均由网友分享,本站只负责收集不承担任何技术及版权问题
3、如本帖侵犯到任何版权问题,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除下载链接并致以最深的歉意
4、本帖部分内容转载自其它媒体,但并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责
5、一经注册为本站会员,一律视为同意网站规定,本站管理员及版主有权禁止违规用户
6、其他单位或个人使用、转载或引用本文时必须同时征得该帖子作者和IT资源小站的同意
7、IT资源小站管理员和版主有权不事先通知发贴者而删除本文
评论0