题目描述
定义构造三叉搜索树规则如下:
每个节点都存有一个数,当插入一个新的数时,从根节点向下寻找,直到找到一个合适的空节点插入。查找的规则是:
- 如果数小于节点的数减去500,则将数插入节点的左子树
- 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
- 否则,将数插入节点的中子树
给你一系列数,请按以上规则,按顺序将数插入树中,构建出一棵三叉搜索树,最后输出树的高度。
输入描述
第一行为一个数 N,表示有 N 个数,1 ≤ N ≤ 10000
第二行为 N 个空格分隔的整数,每个数的范围为[1,10000]
输出描述
输出树的高度(根节点的高度为1)
用例
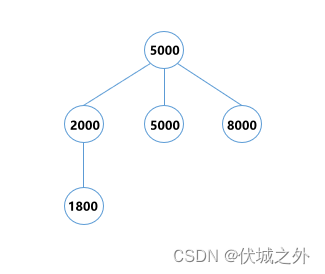
| 输入 | 5 5000 2000 5000 8000 1800 |
| 输出 | 3 |
| 说明 |
最终构造出的树如下,高度为3:
|
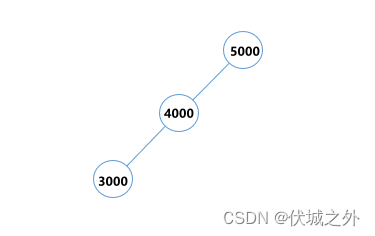
| 输入 | 3 5000 4000 3000 |
| 输出 | 3 |
| 说明 |
最终构造出的树如下,高度为3:
|
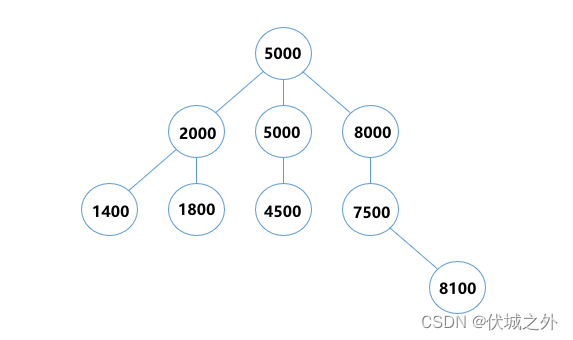
| 输入 | 9 5000 2000 5000 8000 1800 7500 4500 1400 8100 |
| 输出 | 4 |
| 说明 |
最终构造出的树如下,高度为4:
|
题目解析
本题应该只是需要模拟出三叉树结构,以及根据指定的逻辑进行插入新节点。
三叉树节点的数据结构定义如下:
{
val, // 节点值
height,// 节点所在高度,
left,// 左子树根节点,
right,// 右子树根节点,
mid,// 中子树根节点
}
三叉树的数据结构定义如下:
{
root,// 根节点
height,// 树的高度
}
三叉树插入新节点node逻辑:
- 如果三叉树为空,则三叉树根节点root = 新节点node
- 如果三叉树不为空,则从三叉树根节点作为比较节点cur开始比较:
- 如果 node.val < cur.val – 500,则node应该插入到cur节点的左子树中,
若 cur 节点不存在左子树,那么 node 就作为 cur 节点的左子树根节点,且node.height = cur.height + 1
若 cur 节点存在左子树,那么 cur = cur.left,继续和 node 比较 - 如果 node.val > cur.val + 500,则node应该插入到cur节点的右子树中,
若 cur 节点不存在右子树,那么 node 就作为 cur 节点的右子树根节点,且node.height = cur.height + 1
若 cur 节点存在右子树,那么 cur = cur.right,继续和 node 比较 - 其他情况,则 node 应该插入到 cur 节点的中子树中,
若 cur 节点不存在中子树,那么 node 就作为 cur 节点的中子树根节点,且且node.height = cur.height + 1
若 cur 节点存在中子树,那么 cur = cur.mid,继续和 node 比较
在上面比较过程,始终保留最大的node.height作为tree.height。
JS算法源码
const rl = require("readline").createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
var iter = rl[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
void (async function () {
class TreeNode {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val; // 节点值
this.height = undefined; // 节点所在高度
this.left = null; // 左子树
this.mid = null; // 中子树
this.right = null; // 右子树
}
}
class Tree {
constructor() {
this.root = null; // 树的根节点
this.height = 0; // 树的高度
}
add(val) {
const node = new TreeNode(val);
if (this.root == null) {
// 如果树是空的,则当前创建的节点将作为根节点
node.height = 1; // 根节点的高度为1
this.root = node;
this.height = 1;
} else {
// 如果树不是空的,则从根节点开始比较
let cur = this.root;
while (true) {
// 假设创建的节点node是当前节点cur的子节点,则node节点高度值=cur节点高度值+1
node.height = cur.height + 1;
// 如果创建的node进入新层,则更新树的高度
this.height = Math.max(node.height, this.height);
if (val < cur.val - 500) {
// 如果数小于节点的数减去500,则将数插入cur节点的左子树
if (cur.left == null) {
// 如果cur节点没有左子树,则node作为cur节点的左子树
cur.left = node;
// 停止探索
break;
} else {
// 否则继续探索
cur = cur.left;
}
} else if (val > cur.val + 500) {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur.right == null) {
cur.right = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
}
} else {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur.mid == null) {
cur.mid = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur.mid;
}
}
}
}
}
}
const n = parseInt(await readline());
const tree = new Tree();
const nums = (await readline()).split(" ").map(Number);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tree.add(nums[i]);
}
console.log(tree.height);
})();
Java算法源码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static class TreeNode {
int val; // 节点值
int height; // 节点所在高度
TreeNode left; // 左子树
TreeNode mid; // 中子树
TreeNode right; // 右子树
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
static class Tree {
TreeNode root; // 树的根节点
int height; // 树的高度
public void add(int val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
if (this.root == null) {
// 如果树是空的,则当前创建的节点将作为根节点
node.height = 1; // 根节点的高度为1
this.root = node;
this.height = 1;
} else {
// 如果树不是空的,则从根节点开始比较
TreeNode cur = this.root;
while (true) {
// 假设创建的节点node是当前节点cur的子节点,则node节点高度值=cur节点高度值+1
node.height = cur.height + 1;
// 如果创建的node进入新层,则更新树的高度
this.height = Math.max(node.height, this.height);
if (val < cur.val - 500) {
// 如果数小于节点的数减去500,则将数插入cur节点的左子树
if (cur.left == null) {
// 如果cur节点没有左子树,则node作为cur节点的左子树
cur.left = node;
// 停止探索
break;
} else {
// 否则继续探索
cur = cur.left;
}
} else if (val > cur.val + 500) {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur.right == null) {
cur.right = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
}
} else {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur.mid == null) {
cur.mid = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur.mid;
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Tree tree = new Tree();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
tree.add(num);
}
System.out.println(tree.height);
}
}
Python算法源码
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val # 节点值
self.height = None # 节点所在高度
self.left = None # 左子树
self.mid = None # 中子树
self.right = None # 右子树
class Tree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None # 树的根节点
self.height = 0 # 树的高度
def add(self, val):
node = TreeNode(val)
if self.root is None:
# 如果树是空的,则当前创建的节点将作为根节点
node.height = 1 # 根节点的高度为1
self.root = node
self.height = 1
else:
# 如果树不是空的,则从根节点开始比较
cur = self.root
while True:
# 假设创建的节点node是当前节点cur的子节点,则node节点高度值=cur节点高度值+1
node.height = cur.height + 1
# 如果创建的node进入新层,则更新树的高度
self.height = max(node.height, self.height)
if val < cur.val - 500:
# 如果数小于节点的数减去500,则将数插入cur节点的左子树
if cur.left is None:
# 如果cur节点没有左子树,则node作为cur节点的左子树
cur.left = node
# 停止探索
break
else:
# 否则继续探索
cur = cur.left
elif val > cur.val + 500:
# 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if cur.right is None:
cur.right = node
break
else:
cur = cur.right
else:
# 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if cur.mid is None:
cur.mid = node
break
else:
cur = cur.mid
def getResult():
n = int(input())
nums = list(map(int, input().split()))
tree = Tree()
for num in nums:
tree.add(num)
return tree.height
print(getResult())C算法源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
typedef struct TreeNode {
int val; // 节点值
int height; // 节点所在高度
struct TreeNode *left; // 左子树
struct TreeNode *mid; // 中子树
struct TreeNode *right; // 右子树
} TreeNode;
TreeNode *new_TreeNode(int val) {
TreeNode *node = (TreeNode *) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
node->val = val;
node->height = 0;
node->left = NULL;
node->mid = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
typedef struct Tree {
TreeNode *root; // 树的根节点
int height; // 树的高度
} Tree;
Tree *new_Tree() {
Tree *tree = (Tree *) malloc(sizeof(Tree));
tree->root = NULL;
tree->height = 0;
return tree;
}
void add_Tree(Tree *tree, int val) {
TreeNode *node = new_TreeNode(val);
if (tree->root == NULL) {
// 如果树是空的,则当前创建的节点将作为根节点
node->height = 1; // 根节点的高度为1
tree->root = node;
tree->height = 1;
} else {
// 如果树不是空的,则从根节点开始比较
TreeNode *cur = tree->root;
while (1) {
// 假设创建的节点node是当前节点cur的子节点,则node节点高度值=cur节点高度值+1
node->height = cur->height + 1;
// 如果创建的node进入新层,则更新树的高度
tree->height = MAX(node->height, tree->height);
if (val < cur->val - 500) {
// 如果数小于节点的数减去500,则将数插入cur节点的左子树
if (cur->left == NULL) {
// 如果cur节点没有左子树,则node作为cur节点的左子树
cur->left = node;
// 停止探索
break;
} else {
// 否则继续探索
cur = cur->left;
}
} else if (val > cur->val + 500) {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur->right == NULL) {
cur->right = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur->right;
}
} else {
// 如果数大于节点的数加上500,则将数插入节点的右子树
if (cur->mid == NULL) {
cur->mid = node;
break;
} else {
cur = cur->mid;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
Tree *tree = new_Tree();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
add_Tree(tree, num);
}
printf("%dn", tree->height);
return 0;
}免责声明:
1、IT资源小站为非营利性网站,全站所有资料仅供网友个人学习使用,禁止商用
2、本站所有文档、视频、书籍等资料均由网友分享,本站只负责收集不承担任何技术及版权问题
3、如本帖侵犯到任何版权问题,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除下载链接并致以最深的歉意
4、本帖部分内容转载自其它媒体,但并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责
5、一经注册为本站会员,一律视为同意网站规定,本站管理员及版主有权禁止违规用户
6、其他单位或个人使用、转载或引用本文时必须同时征得该帖子作者和IT资源小站的同意
7、IT资源小站管理员和版主有权不事先通知发贴者而删除本文
评论0