题目描述
给定一个二维数组M行N列,二维数组里的数字代表图片的像素,为了简化问题,仅包含像素1和5两种像素,每种像素代表一个物体,2个物体相邻的格子为边界,求像素1代表的物体的边界个数。
像素1代表的物体的边界指与像素5相邻的像素1的格子,边界相邻的属于同一个边界,相邻需要考虑8个方向(上,下,左,右,左上,左下,右上,右下)。
其他约束
地图规格约束为:
0<M<100
0<N<100
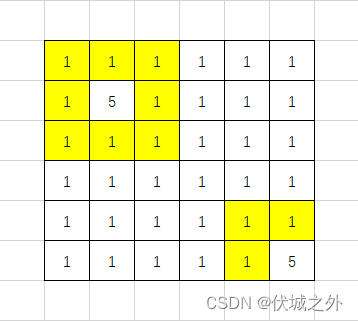
1)如下图,与像素5的格子相邻的像素1的格子(0,0)、(0,1)、(0,2)、(1,0)、(1,2)、(2,0)、(2,1)、(2,2)、(4,4)、(4,5)、(5,4)为边界,另(0,0)、(0,1)、(0,2)、(1,0)、(1,2)、(2,0)、(2,1)、(2,2)相邻,为1个边界,(4,4)、(4,5)、(5,4)相邻,为1个边界,所以下图边界个数为2。
2)如下图,与像素5的格子相邻的像素1的格子(0,0)、(0,1)、(0,2)、(1,0)、(1,2)、(2,0)、(2,1)、(2,2)、(3,3)、(3,4)、(3,5)、(4,3)、(4,5)、(5,3)、(5,4)、(5,5)为边界,另这些边界相邻,所以下图边界个数为1。
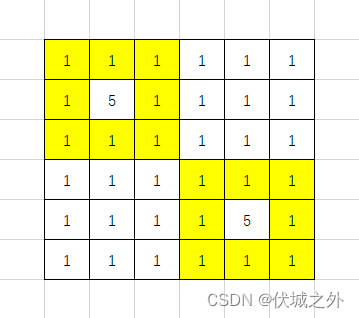
注:(2,2)、(3,3)相邻。
输入描述
第一行,行数M,列数N
第二行开始,是M行N列的像素的二维数组,仅包含像素1和5
输出描述
像素1代表的物体的边界个数。
如果没有边界输出0(比如只存在像素1,或者只存在像素5)。
用例
| 输入 | 6 61 1 1 1 1 11 5 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 5 |
| 输出 | 2 |
| 说明 | 参考题目描述部分 |
| 输入 | 6 61 1 1 1 1 11 5 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 5 11 1 1 1 1 1 |
| 输出 | 1 |
| 说明 | 参考题目描述部分 |
题目解析
本题可以使用并查集。
有几个像素5,我们就可以先假设有几个不相邻的边界。
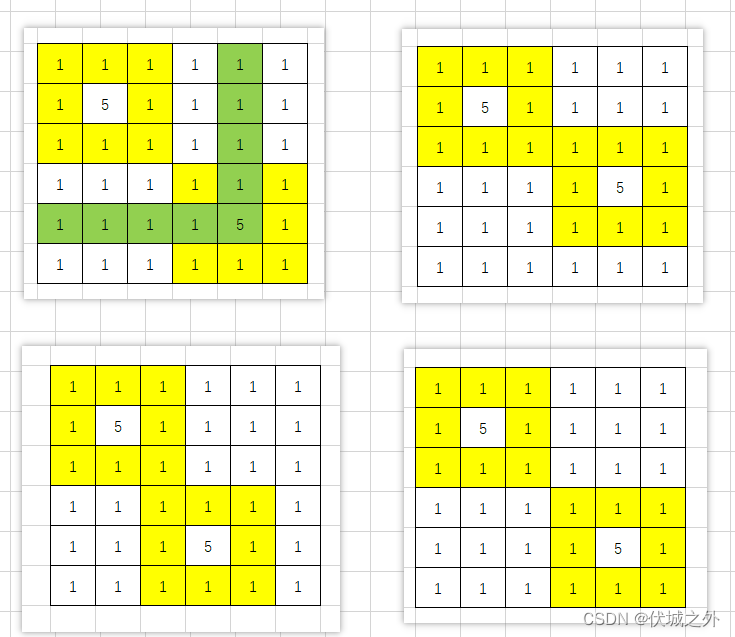
而判断两个边界相邻的条件是:两个像素5坐标满足:|x1-x2| <=3 && |y1-y2| <=3
即如上图绿色线就是另一个像素5的移动范围边界。
因此,本题可以转化为求解像素5是否联通的并查集求解。
2023.10.20
上面思路其实存在一定偏差。
因为本题要求解的是:像素1代表的物体的边界个数。我们可以看一个例子:
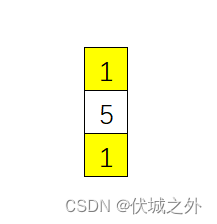
上图所示,应该存在几个边界呢?
如果按照前面思路,则只有1个边界。前面思路其实是以像素5为核心,将像素5周围的像素1统一视为一个边界,但是这是不符合题意的,因为题目要求说:
像素1代表的物体的边界指与像素5相邻的像素1的格子,边界相邻的属于同一个边界
而上面图示中,两个像素1格子是不相邻的,因此不能算同一边界。
我的解题思路如下:
首先,遍历矩阵,将所有像素5相邻的像素1(边界)坐标都取出来。
然后,利用并查集,对这些边界像素1格子进行合并,合并规则是:
两个格子的横向、纵向距离均小于等于1,即为相邻,即可合并。
Java算法源码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] matrix = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(getResult(matrix, m, n));
}
public static int getResult(int[][] matrix, int m, int n) {
// 上、下、左、右、左上、左下、右上、右下的横坐标、纵坐标偏移量
int[][] offsets = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
// 记录所有边界位置
HashSet<Integer> brands = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 如果当前点是像素5
if (matrix[i][j] == 5) {
// 遍历像素5的相邻位置
for (int[] offset : offsets) {
int newI = i + offset[0];
int newJ = j + offset[1];
// 如果该位置不越界,且为像素1,则是边界
if (newI >= 0 && newI < m && newJ >= 0 && newJ < n && matrix[newI][newJ] == 1) {
brands.add(newI * n + newJ);
}
}
}
}
}
ArrayList<Integer> brands_list = new ArrayList<>(brands);
int k = brands_list.size();
// 使用并查集,对所有边界位置进行合并
UnionFindSet ufs = new UnionFindSet(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int x1 = brands_list.get(i) / n;
int y1 = brands_list.get(i) % n;
for (int j = i + 1; j < k; j++) {
int x2 = brands_list.get(j) / n;
int y2 = brands_list.get(j) % n;
// 如果两个边界像素1的位置 横向、纵向距离均小于1,则相邻,可以进行合并
if (Math.abs(x1 - x2) <= 1 && Math.abs(y1 - y2) <= 1) {
ufs.union(i, j);
}
}
}
return ufs.count;
}
}
class UnionFindSet {
int[] fa;
int count;
public UnionFindSet(int n) {
this.count = n;
this.fa = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) this.fa[i] = i;
}
public int find(int x) {
if (x != this.fa[x]) {
return (this.fa[x] = this.find(this.fa[x]));
}
return x;
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int x_fa = this.find(x);
int y_fa = this.find(y);
if (x_fa != y_fa) {
this.fa[y_fa] = x_fa;
this.count--;
}
}
}
JS算法源码
const rl = require("readline").createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
var iter = rl[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
void (async function () {
const [m, n] = (await readline()).split(" ").map(Number);
const matrix = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
matrix.push((await readline()).split(" ").map(Number));
}
console.log(getBrandCount(matrix, m, n));
})();
function getBrandCount(matrix, m, n) {
// 上、下、左、右、左上、左下、右上、右下的横坐标、纵坐标偏移量
const offsets = [
[-1, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, -1],
[0, 1],
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, -1],
[1, 1],
];
// 记录所有边界位置
const brands = new Set();
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 如果当前点是像素5
if (matrix[i][j] === 5) {
// 遍历像素5的相邻位置
for (let offset of offsets) {
const newI = i + offset[0];
const newJ = j + offset[1];
// 如果该位置不越界,且为像素1,则是边界
if (
newI >= 0 &&
newI < m &&
newJ >= 0 &&
newJ < n &&
matrix[newI][newJ] == 1
) {
brands.add(newI * n + newJ);
}
}
}
}
}
const brands_list = [...brands];
const k = brands_list.length;
// 使用并查集,对所有边界位置进行合并
const ufs = new UnionFindSet(k);
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
const x1 = Math.floor(brands_list[i] / n);
const y1 = brands_list[i] % n;
for (let j = i + 1; j < k; j++) {
const x2 = Math.floor(brands_list[j] / n);
const y2 = brands_list[j] % n;
// 如果两个边界像素1的位置 横向、纵向距离均小于1,则相邻,可以进行合并
if (Math.abs(x1 - x2) <= 1 && Math.abs(y1 - y2) <= 1) {
ufs.union(i, j);
}
}
}
return ufs.count;
}
class UnionFindSet {
constructor(n) {
this.fa = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.fa.push(i);
}
this.count = n;
}
find(x) {
if (x !== this.fa[x]) {
this.fa[x] = this.find(this.fa[x]);
return this.fa[x];
}
return x;
}
union(x, y) {
let x_fa = this.find(x);
let y_fa = this.find(y);
if (x_fa !== y_fa) {
this.fa[y_fa] = x_fa;
this.count--;
}
}
}
Python算法源码
# 输入获取
m, n = map(int, input().split())
matrix = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(m)]
# 并查集
class UnionFindSet:
def __init__(self, n):
self.fa = [idx for idx in range(n)]
self.count = n
def find(self, x):
if x != self.fa[x]:
self.fa[x] = self.find(self.fa[x])
return self.fa[x]
return x
def union(self, x, y):
x_fa = self.find(x)
y_fa = self.find(y)
if x_fa != y_fa:
self.fa[y_fa] = x_fa
self.count -= 1
# 算法入口
def getResult():
# 上、下、左、右、左上、左下、右上、右下的横坐标、纵坐标偏移量
offsets = ((-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1))
# 记录所有边界位置
brands = set()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
# 如果当前点是像素5
if matrix[i][j] == 5:
# 遍历像素5的相邻位置
for offset in offsets:
newI = i + offset[0]
newJ = j + offset[1]
# 如果该位置不越界,且为像素1,则是边界
if m > newI >= 0 and n > newJ >= 0 and matrix[newI][newJ] == 1:
brands.add(newI * n + newJ)
brands_list = list(brands)
k = len(brands_list)
# 使用并查集,对所有边界位置进行合并
ufs = UnionFindSet(k)
for i in range(k):
x1 = brands_list[i] // n
y1 = brands_list[i] % n
for j in range(i + 1, k):
x2 = brands_list[j] // n
y2 = brands_list[j] % n
# 如果两个边界像素1的位置 横向、纵向距离均小于1,则相邻,可以进行合并
if abs(x1 - x2) <= 1 and abs(y1 - y2) <= 1:
ufs.union(i, j)
return ufs.count
# 算法调用
print(getResult())
免责声明:
评论0