题目描述
在一个地图中(地图由n*n个区域组成),有部分区域被感染病菌。 感染区域每天都会把周围(上下左右)的4个区域感染。 请根据给定的地图计算,多少天以后,全部区域都会被感染。 如果初始地图上所有区域全部都被感染,或者没有被感染区域,返回-1
输入描述
一行N*N个数字(只包含0,1,不会有其他数字)表示一个地图,数字间用,分割,0表示未感染区域,1表示已经感染区域 每N个数字表示地图中一行,输入数据共表示N行N列的区域地图。
例如输入1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,表示地图
1,0,1
0,0,0
1,0,1
输出描述
一个整数,表示经过多少天以后,全部区域都被感染 1<=N<200
用例
| 输入 | 1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1 |
| 输出 | 2 |
| 说明 | 1天以后,地图中仅剩余中心点未被感染;2天以后,全部被感染。 |
| 输入 | 0,0,0,0 |
| 输出 | -1 |
| 说明 | 无感染区域 |
| 输入 | 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 |
| 输出 | -1 |
| 说明 | 全部都感染 |
题目解析
自测用例:0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0
一共8×8个区域
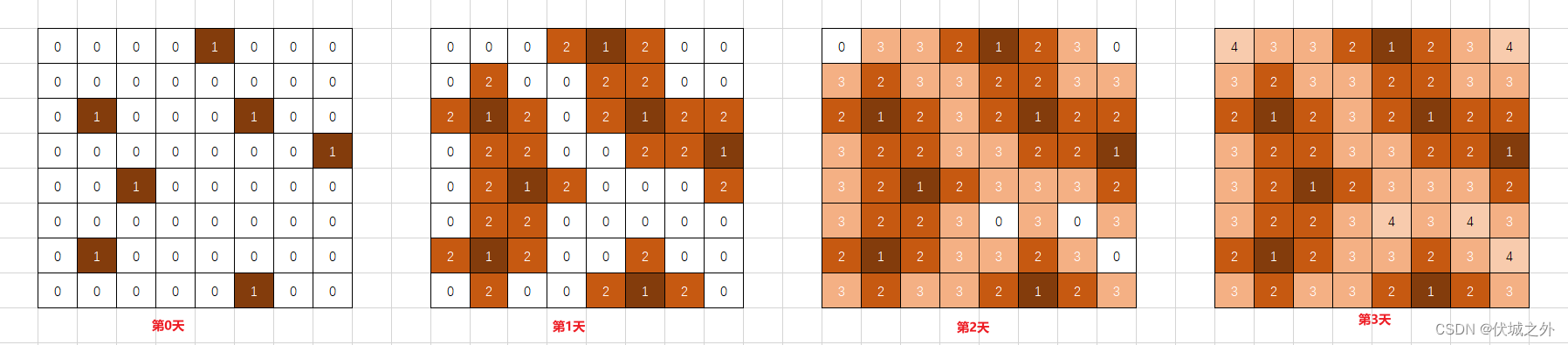
感染区传播过程如上图所示。
本题其实就是图结构的多源BFS。
每个感染区就是图结构中需要进行广度优先搜索的起点。感染区就相当于我们往水面扔了一颗石子,广度优先搜索就相当于荡起的一圈涟漪。
本题的广度优先搜索是基于队列实现的。
创建一个队列queue,初始时,遍历矩阵,找到所有感染区位置,并加入队列。
queue初始化完成后,我们对queue进行出队操作,每一个出队元素就是一个感染区位置,我们需要将其上下左右的区域全部改为感染区,并将新的感染区入队queue。
这样的话才能保证 第一批感染区 的传播才能优先进行,达到广度优先搜索的目的。
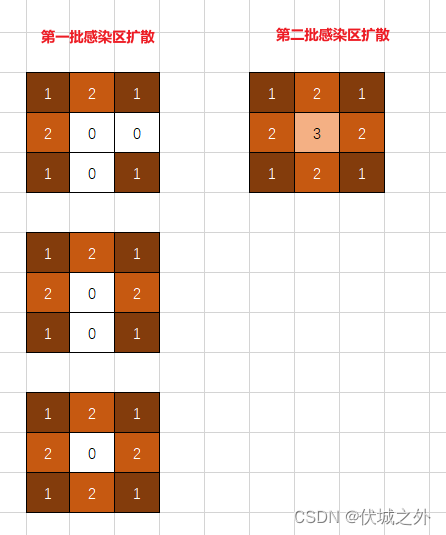
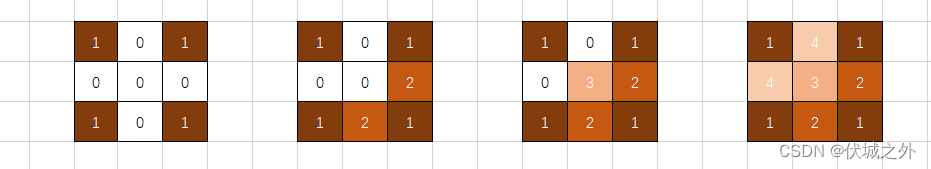
我们再举一个例子,如果采用stack栈来保存感染区的话,则必然先弹栈一个感染区位置,然后将其上下左右区域感染,这个过程中,将新的感染区压栈,而之后再次弹栈,必然是第二批的感染区位置,也就是后进先出,这将会产生深度优先搜索的效果。
最终会产生如下效果
了解图的多源广度优先搜索的实现后,我们就需要考虑如何统计感染时间了,这里我们可以将感染区标记和感染时间捆绑在一起,比如第0天的新增感染区标记为1(即矩阵初始时元素1),第1天的新增感染区标记为2,这个标记是我们广度优先搜索过程中,遍历每个感染区位置上下左右时标记的。
因此,最后一次被标记的时间就是感染全区的时间,但是要减去1,因为我们是第1天标记为2了,因此第n天标记为n+1了。
2023.06.08
上面统计天数的方案,是将天数和矩阵元素值耦合起来,即矩阵元素格子内的值是几,就代表该格子是第几天被感染的。
下面提供一种新方案来统计天数,我们知道,初始时,第一批(第一天)感染区都被统计到了queue中,之后进入bfs逻辑后,我们将新增的感染区也记录到了queue里面,这导致不同天的感染区都被记录到了一起,因此不好区分。
我们可以选择创建一个新的newQueue,来记录新增感染区,比如我们可以遍历queue,来讲queue中感染区扩散出去的新感染区都放到newQueue,如果queue中统计的是第一天的感染区,那么newQueue中统计的就是第二天的感染区。
这样的话,就可以将不同天数的感染区分开统计了。
最后为了保证bfs的正常运行,我们只要将newQueue赋值给queue,进行下一轮感染即可。
而这个过程中,每遍历完queue,就相当于day+1
Java算法源码
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Integer[] arr =
Arrays.stream(sc.nextLine().split(",")).map(Integer::parseInt).toArray(Integer[]::new);
System.out.println(getResult(arr));
}
public static int getResult(Integer[] arr) {
// 题目说会输入n*n个值
int n = (int) Math.sqrt(arr.length);
// 将一维arr输入转为二维矩阵matrix
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n];
// 将矩阵中所有感染区域位置记录到queue中,这里选择queue先进先出的原因是保证当天的感染区域并发扩散
LinkedList<Integer[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = arr[i * n + j];
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) queue.add(new Integer[] {i, j});
}
}
// 全是感染区,或全是健康区
if (queue.size() == 0 || queue.size() == arr.length) {
return -1;
}
// 健康区个数
int healthy = arr.length - queue.size();
// 上下左右偏移量
int[][] offsets = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
// day用于统计感染全部花费的时间
int day = 0;
// 如果健康区个数为0,说明感染完了
while (queue.size() > 0 && healthy > 0) {
LinkedList<Integer[]> newQue = new LinkedList<>();
// 遍历完当前queue的所有感染区,即过去一天
for (Integer[] tmp : queue) {
int x = tmp[0], y = tmp[1];
for (int[] offset : offsets) {
int newX = x + offset[0];
int newY = y + offset[1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < n && newY >= 0 && newY < n && matrix[newX][newY] == 0) {
matrix[newX][newY] = 1;
healthy--;
// 新增感染区加到newQue中,不影响queue的当前遍历
newQue.add(new Integer[] {newX, newY});
}
}
}
day++;
queue = newQue;
}
return day;
}
}
JS算法源码
/* JavaScript Node ACM模式 控制台输入获取 */
const readline = require("readline");
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
rl.on("line", (line) => {
const arr = line.split(",").map(Number);
console.log(getResult(arr));
});
function getResult(arr) {
// 题目说会输入n*n个值
const n = Math.sqrt(arr.length);
// 将一维输入转为二维矩阵
const matrix = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(0));
// 将矩阵中所有感染区域位置记录到queue中,这里选择queue先进先出的原因是保证当天的感染区域并发扩散
let queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = arr[i * n + j];
if (matrix[i][j] === 1) queue.push([i, j]);
}
}
// 全是感染区,或全是健康区
if (queue.length === 0 || queue.length === arr.length) {
return -1;
}
// 健康区个数
let healthy = arr.length - queue.length;
// 上下左右位置偏移量
const offsets = [
[-1, 0], // 上
[1, 0], // 下
[0, -1], // 左
[0, 1], // 右
];
// day用于统计感染全部花费的时间
let day = 0;
// 如果健康区个数为0,说明感染完了
while (queue.length && healthy) {
const newQueue = [];
// 遍历完当前queue的所有感染区,即过去一天
for (const [x, y] of queue) {
for (let [offsetX, offsetY] of offsets) {
const newX = x + offsetX;
const newY = y + offsetY;
if (
newX >= 0 &&
newX < n &&
newY >= 0 &&
newY < n &&
matrix[newX][newY] === 0
) {
healthy--;
matrix[newX][newY] = 1;
// 新增感染区加到newQue中,不影响queue的当前遍历
newQueue.push([newX, newY]);
}
}
}
day++;
queue = newQueue;
}
return day;
}
Python算法源码
import math
# 输入获取
arr = list(map(int, input().split(",")))
# 算法入口
def getResult(arr):
# 题目说会输入n*n个值
n = int(math.sqrt(len(arr)))
# 将一维arr输入转为二维矩阵matrix
matrix = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
# 将矩阵中所有感染区域位置记录到queue中,这里选择queue先进先出的原因是保证当天的感染区域并发扩散
queue = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
matrix[i][j] = arr[i * n + j]
if matrix[i][j] == 1:
queue.append([i, j])
# 全是感染区,或全是健康区
if len(queue) == 0 or len(queue) == len(arr):
return -1
# 健康区个数
healthy = len(arr) - len(queue)
# 上下左右偏移量
offsets = ((-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1))
# day用于统计感染全部花费的时间
day = 0
# 如果健康区个数为0,说明感染完了
while len(queue) > 0 and healthy > 0:
newQueue = []
# 遍历完当前queue的所有感染区,即过去一天
for x, y in queue:
for offsetX, offsetY in offsets:
newX = x + offsetX
newY = y + offsetY
if n > newX >= 0 and n > newY >= 0 and matrix[newX][newY] == 0:
healthy -= 1
matrix[newX][newY] = 1
# 新增感染区加到newQue中,不影响queue的当前遍历
newQueue.append([newX, newY])
day += 1
queue = newQueue
return day
# 算法调用
print(getResult(arr))
C算法源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 200
typedef struct ListNode {
int ele;
struct ListNode *next;
} ListNode;
typedef struct {
int size;
ListNode *head;
ListNode *tail;
} LinkedList;
LinkedList *new_LinkedList();
void addLast_LinkedList(LinkedList *link, int ele);
int getResult(const int nums[], int nums_size);
int main() {
int nums[MAX_SIZE * MAX_SIZE];
int nums_size = 0;
while (scanf("%d", &nums[nums_size++])) {
if (getchar() != ',') break;
}
printf("%dn", getResult(nums, nums_size));
return 0;
}
int getResult(const int nums[], int nums_size) {
// 题目说会输入n*n个值
int n = (int) sqrt(nums_size);
// 将一维arr输入转为二维矩阵matrix
int matrix[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
// 将矩阵中所有感染区域位置记录到queue中,这里选择queue先进先出的原因是保证当天的感染区域并发扩散
LinkedList *queue = new_LinkedList();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = nums[i * n + j];
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
addLast_LinkedList(queue, i * n + j);
}
}
}
// 全是感染区,或全是健康区
if (queue->size == 0 || queue->size == nums_size) {
return -1;
}
// 健康区个数
int healthy = nums_size - queue->size;
// 上下左右偏移量
int offsets[4][2] = {{-1, 0},
{1, 0},
{0, -1},
{0, 1}};
// day用于统计感染全部花费的时间
int day = 0;
// 如果健康区个数为0,说明感染完了
while (queue->size > 0 && healthy > 0) {
LinkedList *newQueue = new_LinkedList();
// 遍历完当前queue的所有感染区,即过去一天
ListNode *cur = queue->head;
while (cur != NULL) {
int x = cur->ele / n;
int y = cur->ele % n;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + offsets[i][0];
int newY = y + offsets[i][1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < n && newY >= 0 && newY < n && matrix[newX][newY] == 0) {
matrix[newX][newY] = 1;
healthy--;
// 新增感染区加到newQue中,不影响queue的当前遍历
addLast_LinkedList(newQueue, newX * n + newY);
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
day++;
queue = newQueue;
}
return day;
}
LinkedList *new_LinkedList() {
LinkedList *link = (LinkedList *) malloc(sizeof(LinkedList));
link->size = 0;
link->head = NULL;
link->tail = NULL;
return link;
}
void addLast_LinkedList(LinkedList *link, int ele) {
ListNode *node = (ListNode *) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->ele = ele;
node->next = NULL;
if (link->size == 0) {
link->head = node;
link->tail = node;
} else {
link->tail->next = node;
link->tail = node;
}
link->size++;
}
免责声明:
评论0